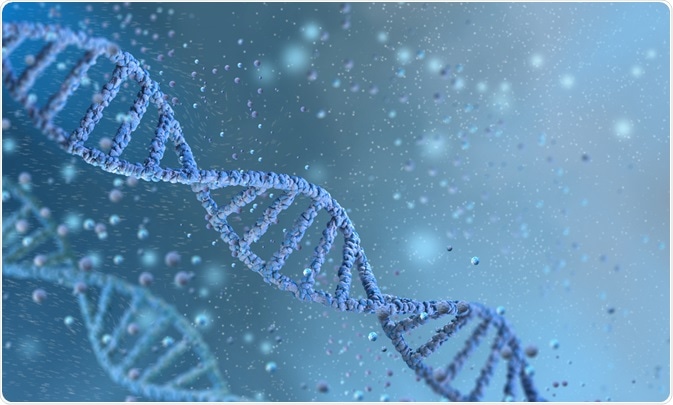
What Concept Is Used to Describe Simple Genetically Defied Activities
Define and describe Genetically Modified Organisms. They learn what role enzymes DNA and genes play in the modification of organisms.
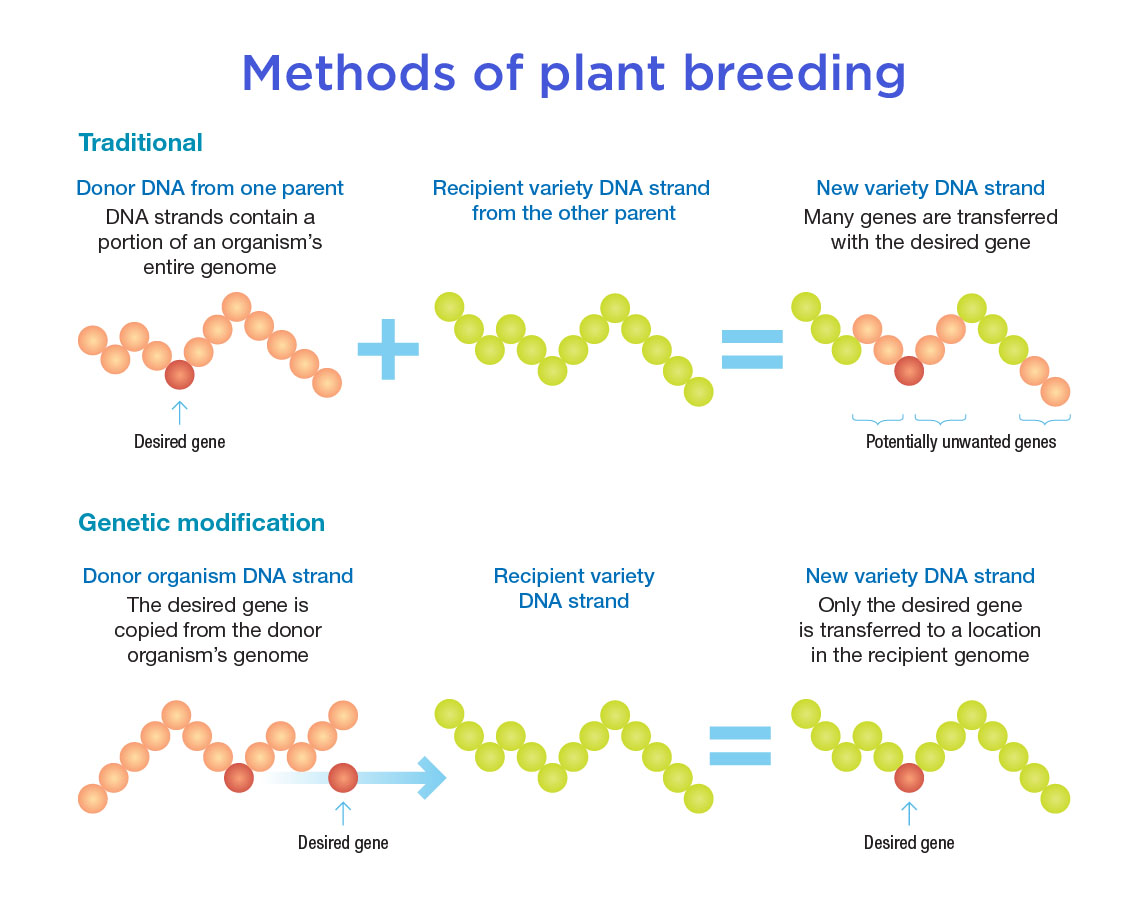
What Is Genetic Modification Curious
Although appearance is helpful in identifying species it does not define species.

. Genetic Terms Use library resources to define the following words and write their definitions using your own words. Inside each cell atoms make up molecules. Genetically modified organisms GMOs are produced using scientific methods that include recombinant DNA technology and reproductive cloning.
Approximately 20 of all vertebrates including 33 of sharks and rays are at risk of extinction. In describing the process the example of a soybean will be used as a guide to each step. Genetic engineering is commonly used in agriculture.
Even very simple single-celled organisms are remarkably complex. According to the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005 a 5-year project begun in 2001 to assess the worlds ecosystems an estimated 1015 of the worlds species will be committed to extinction by 2035. In reproductive cloning a nucleus is extracted from a cell of the individual to be cloned and is inserted into the enucleated cytoplasm of a host egg an enucleated egg is an egg cell that has had its own nucleus removed.
Some crops are engineered to resist pests or herbicides. Tracking these conditions is important for public policy. Cognitive style is thus claimed to be a single dimension on a scale from extreme left-brain to extreme.
Sex is assigned at birth while gender is how a person identifies. Through the introduction of a gene from a different organism. Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application.
Strictly applied the term mitosis is used to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes the structures that carry the genetic information. Organisms are highly organized structures that consist of one or more cells. The field having a genetically altered clonal unit has an enhanced proliferative activity which is the driving force of the entire process.
In systems neuroscience the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making learning fear memory mating addiction feeding and locomotion. The clones diverge at different times creating a relatively large number of. Robert Ornsteins Hemispherical lateralisation concept Carey 1991 commonly called left-brainright-brain theory posits that the left hemisphere of the brain controls logical and analytical operations while the right hemisphere controls holistic intuitive and pictorial activities.
Identity might bring to mind questions of skin color. Appearance isnt everything Organisms may appear to be alike and be different species. Complex molecules are converted to simple molecules with the.
Students construct paper recombinant plasmids to simulate the methods genetic engineers use to create modified bacteria. These in turn make up cell components or organelles. A genetic predisposition sometimes also called genetic susceptibility is an increased likelihood of developing a particular disease based on a persons genetic makeup.
In the early 2000s genetically modified crops covered about one tenth of the worlds farmland. The are several steps in the process of genetic engineering. They learn what genetic engineering means and examples of its applications as well as moral and ethical problems related to its implementation.
Students learn how engineers apply their understanding of DNA to manipulate specific genes to produce desired traits and how engineers have used this practice to address current problems facing humanity. Good living conditions eg housing employment are fundamental to well-being. Both terms are used to describe human identity but in different if related ways.
It helps to produce crops that are stronger or more nutritious than regular crops. Conception generality generalization notion stereotype abstraction cogitation idea. When viewed together these eight characteristics serve to define life.
Others have added vitamins or minerals. These genetic changes contribute to the development of a disease but do not directly. The biological species concept defines a species as members of populations that actually or potentially interbreed in nature not according to similarity of appearance.
Mitosis a process of cell duplication or reproduction during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Virus are simple. Gender encompasses a broad spectrum.
As most people who read textbooks and things know recombinant DNA technology started with pretty simple things--cloning very small pieces of DNA and growing them in bacteria--and has evolved to an enormous field where whole genomes can be cloned and moved from cell to cell to cell using variations of techniques that all would come under genetic engineering as a very. For example Western meadowlarks Sturnella. This step requires that the wanted gene is found.
Describe strategies that are used to manage insect resistance in genetically modified GM crops. 26As the lesions grow in size additional genetic hits arise in the region resulting in various sub-clones within the field. Discuss the biosafety issues involved in the use of genetically engineered microorganism.
The technology is often called modern biotechnology or gene technology sometimes also recombinant DNA. Well-being is a positive outcome that is meaningful for people and for many sectors of society because it tells us that people perceive that their lives are going well. Scientist follow a step by step process in order to alter the DNA of an organism.
For the particular model they work on they isolate a mammal insulin gene and combine it with a bacterias gene sequence plasmid DNA for production of. Word Match Activity. Sex and gender are different.
First a gene is picked that will be altered added or removed. A genetic predisposition results from specific genetic variations that are often inherited from a parent. By unnatural means or through genetic engineering changing or altering an organisms genetic composition without affecting its normal function is Known as GMOs or Either prokaryotes or eukaryotes whose genome is altered in the laboratory using artificial techniques are known as genetically modified organisms Process.
Humans have two sets of 23 chromosomes one set from each parent. Genetically modified GM foods are foods derived from organisms whose genetic material DNA has been modified in a way that does not occur naturally eg. Learn more about this topic biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.

Gene Vs Allele Definition Difference And Comparison Technology Networks

Thinking And Intelligence Flash Cards For Psychology Psychology Vocabulary Flash Cards Psychology Student

Detecting Local Genetic Correlations With Scan Statistics Nature Communications

Pin By Alexandria Reber On Home Phrase Words Personalized Items

How Science And Genetics Are Reshaping The Race Debate Of The 21st Century Science In The News
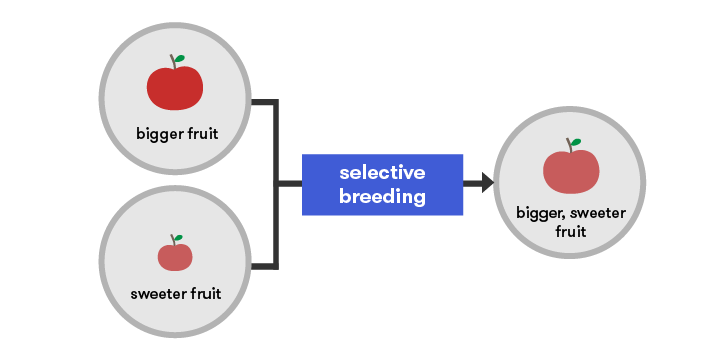
What Is Genetic Modification Curious
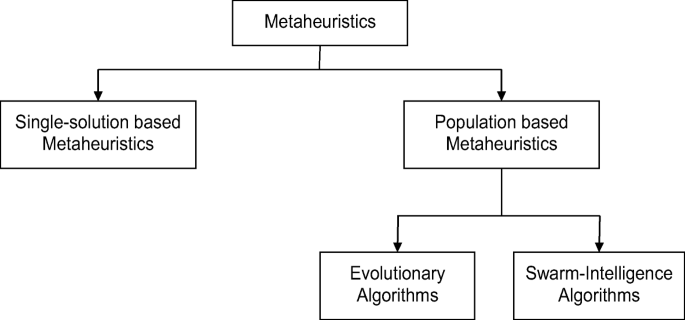
A Review On Genetic Algorithm Past Present And Future Springerlink

Genetic Engineering Don T Memorise Youtube

Neurodevelopmental Disorders From Genetics To Functional Pathways Trends In Neurosciences
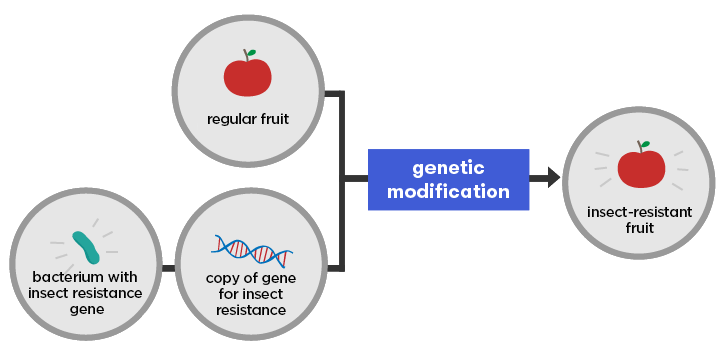
What Is Genetic Modification Curious

Genetic Engineering An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

What Is Genetic Testing The Complete Wired Guide Wired

Genes And Identity Human Genetic Engineering Learn Science At Scitable

Preimplantation Genetic Testing For Aneuploidy A Castle Built On Sand Trends In Molecular Medicine

The Definition Of Gene Therapy Has Changed

Pin By Alexandria Reber On Home Phrase Words Personalized Items

